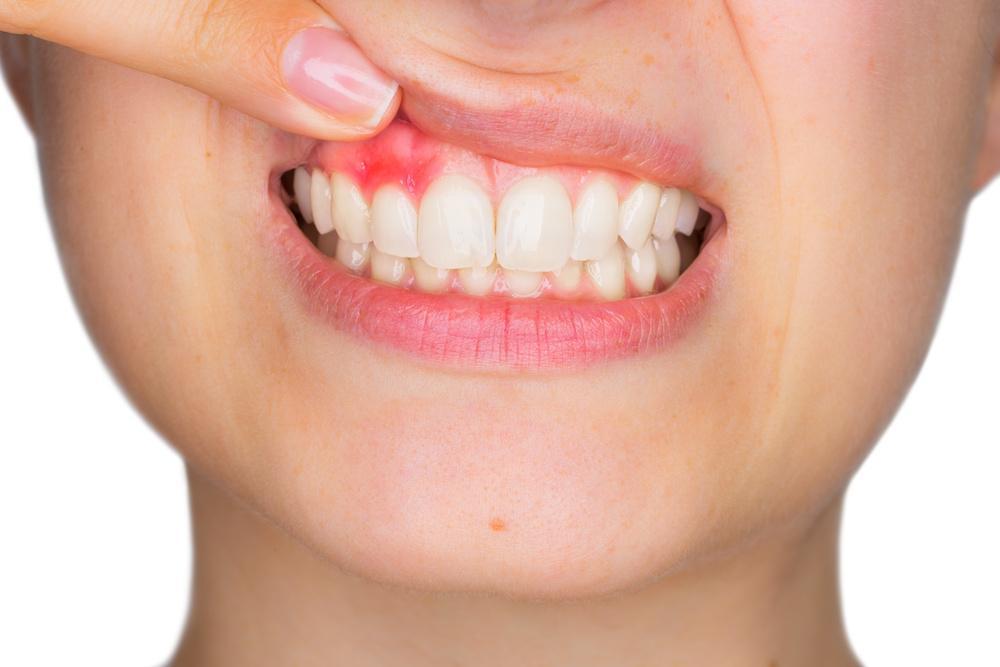
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of periodontitis, it is important to see a periodontist in Dedham, MA right away. There are a number of treatments available for periodontitis, and early treatment can help prevent the condition from progressing and causing serious damage to your teeth and gums.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is an advanced stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums. It typically begins with gingivitis, a milder form of gum disease caused by the buildup of plaque – a sticky film of bacteria – on the teeth. If not addressed, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, leading to more severe consequences for oral health.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
The symptoms of periodontitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Receding gums
- Loose or sensitive teeth
- Bad breath
- A change in the way your teeth fit together
Risk Factors for Periodontitis
There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing periodontitis, including:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking
- Family history of gum disease
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes
- Weakened immune system
Complications of Periodontitis
If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to a number of serious complications, including:
- Tooth loss
- Bone loss
- Infection
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Diabetes complications
Preventing Periodontitis
The best way to prevent periodontitis is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing once a day, and seeing your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings. You can also help prevent periodontitis by:
- Quitting smoking
- Controlling your blood sugar if you have diabetes
- Getting treatment for any medical conditions that you have
Treating Periodontitis
There are several treatments available for periodontitis, depending on the severity of the condition. Mild periodontitis can often be treated with professional cleaning and scaling, which removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line. More severe cases of periodontitis may require additional treatments, such as:
- Antibiotic therapy
- Surgery to remove damaged gum tissue and bone
- Gum grafts to replace lost gum tissue
Conclusion
Periodontitis is a serious gum disease that can lead to a number of health problems. However, it is also a preventable condition. By practicing good oral hygiene and seeing your dentist for regular checkups, you can help prevent periodontitis and keep your gums and teeth healthy.